 Linear bearing rails are linear rails that utilize rolling element bearings, ball bearings, or roller bearings. The moving parts within linear bearing rails are significant in mechanical engineering, as they provide greater efficiency and effectiveness to linear guide systems. Linear bearing rails are more durable, versatile, and have a higher load capacity than other options for linear rails, specifically when compared with linear rods, and are the ideal solution for linear guide systems in manufacturing and other applications.
Linear bearing rails are linear rails that utilize rolling element bearings, ball bearings, or roller bearings. The moving parts within linear bearing rails are significant in mechanical engineering, as they provide greater efficiency and effectiveness to linear guide systems. Linear bearing rails are more durable, versatile, and have a higher load capacity than other options for linear rails, specifically when compared with linear rods, and are the ideal solution for linear guide systems in manufacturing and other applications.
Types of Linear Bearing Rails
There are several different types of linear bearing rails, and the majority of linear bearing rails can be customized to fit the needs of your application.


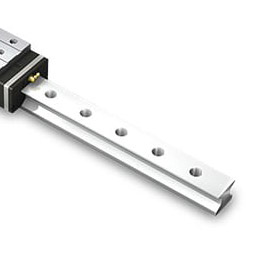
Components of Linear Bearing Rails
Linear bearing rails can be customized for specific applications, but will all have similar components.

Rail Material
Linear guide rails are usually composed of hardened, high-strength, galvanized steel. The metal is manufactured using a cold drawing process, and will be shaped and profiled to the necessary specifications. Steel is used as it can resist corrosion, is resistant to cracking, has a long lifespan, and has the necessary strength for the majority of applications. Linear rails can be treated with additional coatings to further resist corrosion, seal out contaminants, and allow for use in a variety of environments. Keeping the seals constantly lubricated is the best way to keep the rail functioning well during heavy use.

Bearing Carriages
Linear bearing carriages work with linear rollers and rails as part of the linear guide system. Linear bearing carriages are used either individually or in combination with multiple rails. The linear bearings will be recirculated through the carriages. The load for a linear guide system is often determined by the load capacity of the linear bearing carriage. Linear bearing carriages require lubrication to function well within a linear guide system and keep friction reduced. Linear bearing carriages can be designed for high load capacity, high precision, and low friction.

Seals and Lubrication Systems
While the construction of the rail and bearing carriage is important to the performance of the linear guide system, seals and lubrication are crucial to keeping that performance high. Most linear guide systems have three different seals to protect the system from contamination; the end seal, bottom seal, and inner seal. Additional seals can be added for additional protection in harsh environments. Together, these seals work to keep the linear guide protected and clean. Although linear guide systems have low maintenance requirements, regular lubrication and inspection are necessary to ensure that the systems are functioning properly. There are self-lubricating options that lower maintenance requirements even further, and many linear guide systems incorporate these options.
Selection Criteria for Linear Bearing Rails
When selecting a linear bearing rail for your application, there are several criteria to consider.
Load Capacity and Dynamic Ratings
For any engineering design, determining load capacity is important. The dynamic load calculations are crucial to avoiding failure once the linear guide system is integrated. Load capacity is calculated for both dynamic and static loads. Static loads are the load on the system in a fixed, unmoving position, while dynamic load refers to how the load can be moved through the system. If the load is calculated incorrectly, the system can see increased friction, low precision, and even the failure of the rail. As linear bearing rails are available in a variety of load capacities, it is important to understand the needs of your application before settling on your selection.
Rigidity and Stiffness
The more rigid a linear bearing rail is, the higher the precision due to low deflection of the load. The issue of bending in a linear guide system can have a negative impact on system performance, causing low accuracy and high friction. Applications that require the highest precision will need to choose linear bearing rails with a high degree of rigidity and stiffness. While some applications requiring high load capacity can benefit from flexibility, when precision and performance are also a factor, rigidity and flexibility must be balanced.
Accuracy and Tolerance
Accuracy, and more specifically, the need to maintain high degrees of accuracy over time, are also important when selecting a linear guide rail. For applications demanding precise performance, such as CNC, robotics, and material handling, it is crucial to ensure that the chosen linear bearing rail meets the necessary precision standards. To maintain accuracy over time, the guidance system will need to be installed correctly and maintained throughout the lifespan. Having the system mounted with precision will ensure that the linear guide will operate with a high degree of accuracy-even over time.
Environmental Factors
When selecting linear bearing rails as part of a linear guide system, it is important to consider the environment in which the system will be utilized. Considerations such as temperature, dust and dirt levels, chemical exposure, radiation, vibration, and any other environmental factors will need to be considered. In choosing a linear bearing rail that will operate in one of these environments, resistance to contaminants and corrosion are important. Certain corrosion resistant materials, seals, or finishing treatments can be used on the linear guide system to ensure they will function well in various environmental situations.
Installation and Maintenance
If a linear bearing rail is not installed or maintained properly, it will not function well. It’s essential to employ best practices for installation as well as follow the lubrication and maintenance guidelines.
Installation Best Practices
Installation for linear guide rails include alignment procedures, mounting considerations, and safety precautions. Proper installation should be made on a solid foundation. The guide rails will be balanced, then bolted down. Accurate bolting will ensure that the rails do not move, however, care must be taken to ensure that nothing is overtightened, which can deform or damage the guide rail. When you select your linear guide rail, you will be given explicit installation instructions and best practices to ensure that the linear guide system will perform as expected.
Lubrication and Maintenance Guidelines
NSK engineers have recommended proper lubrication techniques, as well as a regular schedule for lubrication, inspection, and cleaning. Following these techniques and schedule is the best way to ensure that your system is functioning as expected and preventative maintenance can help avoid system failures. Many of the linear guide system components are available in self-lubricating options, making maintenance requirements low, but regular inspection is still important. Most failures in linear motion components are due to misalignment or improper assembly. If the motion is not smooth, looking at the alignment of the rail is the logical first step.
Applications of Linear Bearing Rails
Linear bearing rails are used in a variety of applications and can be customized for any need of these applications.
Machinery and Automation
As automation continues to grow in manufacturing, linear guide systems will become even more prevalent in machining and manufacturing. Linear guide systems are used extensively in CNC machines, conveyor systems, and packaging machinery. Linear bearing rails are lightweight, compact, and perform with a high load capacity. They boast a high degree of precision and accuracy, and can move components throughout a facility very efficiently. Automation requires smooth and repeated motion, and linear bearing rails are able to provide the kind of motion necessary to perform these automated tasks accurately.
Robotics and Automation Systems
Linear bearing rails are ideal for linking production lines, tending to multiple automated and robotic systems, managing pick and place systems, and optimizing production. Robotic arms and manipulators, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and collaborative robots (cobots) all rely on linear motion systems that incorporate linear bearing rails. Linear bearing rails possess the necessary rigidity and durability to sustain smooth and repetitive motion, ensuring a high level of accuracy and the low friction essential for optimal performance. As more tasks become automated and rely on robotics and automation systems, linear bearing rails will become even more important.
3D Printing
In general, linear bearing rails are the preferred component of linear guide systems in 3D printing. Linear bearing rails offer exceptional precision and smooth motion which can improve print quality and reliability. Linear bearing rails play a major role in the precision movement of these linear guide systems, as well as making a positive impact on print quality. Linear bearing rails produce a high degree of accuracy and stability, which is important for 3D printing. Because linear bearing rails are low-maintenance, they will allow 3D printers to operate with minimal downtime.
Industrial Applications
Linear bearing rails have many different industrial applications. As linear bearing rails can be customized for the exact needs of the application, they can be present in nearly every application that relies on linear motion.
Material Handling Systems
Material handling systems often have high load requirements, and linear bearing rails have the load capacity for these systems, as well as low friction, smooth and accurate movement, and the ability to work in a variety of environments. Linear bearing rails are crucial in material handling equipment such as conveyor systems, automated warehouses, and sorting systems, as they offer smooth and precise movement. These systems rely on continuous movement with minimal downtime, and linear bearing rails, being low maintenance, can offer the reliability that is necessary.
Packaging Machinery
 The packaging industry relies on the automation and continuous movement that linear guide systems can provide. Linear bearing rails are employed in packaging machinery for tasks like filling, sealing, labeling, and sorting. The smooth and accurate motion of the linear bearing rail within the linear guide system ensures accurate and efficient packaging processes. As linear bearing rails can be customized for a variety of load-bearing capacities, they work well for the different needs of the packaging industry.
The packaging industry relies on the automation and continuous movement that linear guide systems can provide. Linear bearing rails are employed in packaging machinery for tasks like filling, sealing, labeling, and sorting. The smooth and accurate motion of the linear bearing rail within the linear guide system ensures accurate and efficient packaging processes. As linear bearing rails can be customized for a variety of load-bearing capacities, they work well for the different needs of the packaging industry.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical manufacturing industry has had increased reliance on automation in recent years, with many repetitive tasks moving to automated and robotic systems. Linear bearing rails play a role in the linear guide systems of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment, including tablet presses, liquid filling machines, and automated packaging systems. Pharmaceutical manufacturing has a high degree of regulation and requires precision and accuracy, which linear guide systems can provide with minimal downtime.
Electronics Assembly
Electronics assembly is another industry that is increasingly reliant on automation. Linear bearing rails are used in the assembly of electronic components, such as pick-and-place machines, surface mount technology (SMT) equipment, and automated testing systems.

Laboratory Automation
As with other highly regulated industries, more laboratories are moving to automation for repeated high precision tasks, and linear guide systems can provide the accuracy and smooth motion necessary for laboratory tasks. Linear bearing rails play a crucial role in linear guidance systems for laboratory automation equipment, facilitating tasks such as sample handling, liquid dispensing, and high-throughput screening systems.
Textile Industry
Textile plants rely on machinery and automation that can be provided by linear guide systems. Linear bearing rails contribute to the precision and reliability of textile machinery, including looms, spinning machines, and fabric inspection systems. These machines require high accuracy, smooth motion, and minimal friction for repeated tasks, which can easily be provided by a high-quality linear guide system.
Automated Inspection Systems
Automated inspection systems are becoming more prevalent in many different plants and manufacturing facilities. Linear bearing rails are employed in automated inspection systems for quality control processes, such as vision inspection machines and coordinate measuring machines (CMM). Automated inspection systems demand a high degree of reliability that linear guide systems can provide.
Rail Transportation
Travel along rail systems within a plant or manufacturing setting has always been a primary function of linear guide systems. Linear bearing rails are used in rail transportation systems for most rail transportation applications like door systems, seat adjustments, and automated maintenance equipment that are used in a variety of other industries. Airline and car adjustable seats, sliding and gliding doors, and the like all rely on the smooth motion of linear bearing rails.
Material Cutting and Machining
Material cutting and machining require a high degree of accuracy with low friction, and linear bearing rails, as part of a linear guide system, are crucial to this process. Linear bearing rails are utilized in machines for material cutting and machining processes, such as laser cutting machines, waterjet cutters, and CNC machining centers. Smooth linear motion is extremely important in material cutting and machining, and linear guide systems incorporating linear bearing rails can provide that smooth motion with low friction.
Industrial Robotics
 Industrial robotics are becoming more prevalent in many different industries and have been seen as the answer to many industrial challenges. Collaborative robots (cobots) are present in many manufacturing processes as the automation of processes continues to develop. Linear bearing rails play a critical role in the movement systems of industrial robots used in various industries for tasks like welding, painting, and material handling. These tasks require varying degrees of accuracy and precision, but long-term repeatable linear motion is the key component of industrial robotics.
Industrial robotics are becoming more prevalent in many different industries and have been seen as the answer to many industrial challenges. Collaborative robots (cobots) are present in many manufacturing processes as the automation of processes continues to develop. Linear bearing rails play a critical role in the movement systems of industrial robots used in various industries for tasks like welding, painting, and material handling. These tasks require varying degrees of accuracy and precision, but long-term repeatable linear motion is the key component of industrial robotics.
Renewable Energy
Reliance on renewable energy is growing across a variety of industries. Renewable energy is important to many industries, as measuring the environmental impact of each industry is something that is looked at closely by consumers and regulatory bodies. Linear bearing rails are used in producing and maintaining renewable energy systems such as solar tracking systems and positioning systems in wind turbines. Linear bearing rails help to make these systems possible for a variety of applications.
Dental Equipment Manufacturing
The dental industry, like the medical industry, is making use of linear guide systems in both diagnostic and surgical equipment as well as dental chairs and other dental office equipment. Linear bearing rails contribute to the precision and movement control in the manufacturing of dental equipment, including milling machines and robotic-assisted surgery systems. As the dental field continues to advance, especially in robotic surgery and advanced diagnostics, linear bearing rails will be relied on even more. Low friction, high precision, and smooth motion are all important in both the medical and dental equipment industry.
Emerging Trends in Linear Bearing Rail Technology
Linear bearing rails are adapting to the changes in technology as well as the needs of the industries who utilize linear guide systems.
Integration with Smart Systems
Smart systems use sensor technology and data collection and analysis in order to make use of predictive maintenance practices. Smart systems are meeting the increasing demand for greater connectivity and an increasingly digitized system. The smart system will detect any changes within the system and alert the operator what maintenance, repair, or inspection should take place before a failure can occur, which will reduce downtime. Embedding sensors into the linear guide system itself can incorporate functions that were previously external. Integration into Smart Systems will provide greater ease of use and visibility into the operation.
Lightweight Materials
Materials continue to advance, and linear bearing rails can take advantage of the increasingly lightweight materials available. Aluminum, carbon fiber, and composite options, rather than only stainless steel, are very effective in certain applications where the weight of the linear bearing rail needs to be minimal. Using aluminum or composite for the linear rail will have a significant impact on overall system weight, leading to advancements in lightweight rail technology. These lightweight materials will still have the rigidity, stiffness, low friction, and high accuracy as more traditional options, but are crucial in the aerospace and automotive industries, where excess weight can cause issues
There are many options in materials, design, and installation techniques when you are integrating a linear guide system. Choosing the right linear bearing rail can make a difference in the overall function of your linear guide system. When you choose a linear bearing rail to meet your needs, you can be sure that you will get the precision and accuracy you need from the linear motion system with minimal friction. Working with NSK and our team can help you define your needs from a linear bearing rail and customize a solution that will work with your application. We will help you balance your load capacity, precision, vibration, and environmental needs to find the right linear bearing rail for your linear motion system.
