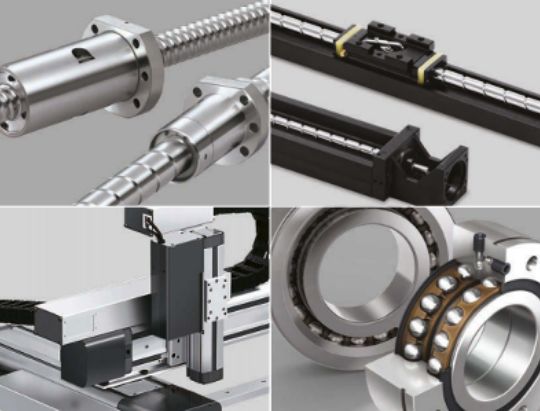
 Linear bearings and rails are two components of a linear guide system, providing smooth and precise linear motion in machinery and equipment across a wide variety of industries and applications. Linear guide systems are relatively simple systems designed to do the simple job of moving things smoothly and safely through a process.
Linear bearings and rails are two components of a linear guide system, providing smooth and precise linear motion in machinery and equipment across a wide variety of industries and applications. Linear guide systems are relatively simple systems designed to do the simple job of moving things smoothly and safely through a process.
There are many types of linear motion bearings, all designed to provide free motion in one direction. The bearings support the load of the carriage during movement, providing a low-friction sliding surface for the guide rail.
The linear bearing is a critical component of the linear guide assembly, as it supports the load of the carriage during the movement along the single axis of the linear rail, which is designed to support the movement.
Linear bearings and rails are used for linear guide systems in medical and laboratory equipment, manufacturing and automation, MFG environments, the transportation industry, and many more applications that rely on precise, smooth, and low-friction linear motion.
Types of Linear Bearings
There are several types of linear bearings used in linear guide systems. When designing the linear guide system for a specific application, the experts will help select the type of bearing that will best support the load.



Linear Rail Systems
Linear rails are an alternative to linear rods and are generally manufactured to be more effective in a linear guide system than linear rods. They have a high tolerance, making them less likely to flex during operation, ensuring the movement is smooth and consistent. There are options for linear rails within linear guide systems.
 Profile Rails: Profile rails, sometimes referred to as square rails, utilize an inner rail and an outer carriage. Profile rails are extremely versatile in linear systems and are suitable for high-precision applications. They can handle high-load applications, supporting the load throughout the length of the rail due to the stiffness of the rail. Profile rails require precise installation and are generally higher cost than other options due to their exceptional performance.
Profile Rails: Profile rails, sometimes referred to as square rails, utilize an inner rail and an outer carriage. Profile rails are extremely versatile in linear systems and are suitable for high-precision applications. They can handle high-load applications, supporting the load throughout the length of the rail due to the stiffness of the rail. Profile rails require precise installation and are generally higher cost than other options due to their exceptional performance.
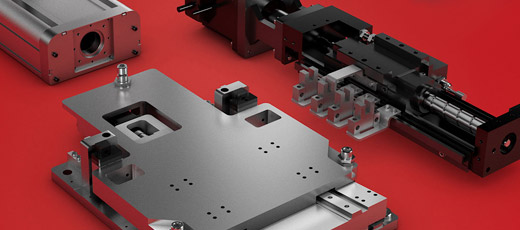 Guideway Systems: Linear guideway systems combine rails and bearings to create complete linear motion solutions. These are among the most extensive and complex solutions for applications requiring linear motion systems, using a circulating rolling element between a profiled rail and a bearing block. Linear guideway systems are used in actuators and actuator systems. NSK has recently released linear guideway systems consisting of AXIS actuators, monocarriers, and robot modules. Linear guideway systems achieve high precision and great accuracy while carrying loads.
Guideway Systems: Linear guideway systems combine rails and bearings to create complete linear motion solutions. These are among the most extensive and complex solutions for applications requiring linear motion systems, using a circulating rolling element between a profiled rail and a bearing block. Linear guideway systems are used in actuators and actuator systems. NSK has recently released linear guideway systems consisting of AXIS actuators, monocarriers, and robot modules. Linear guideway systems achieve high precision and great accuracy while carrying loads.
Applications of Linear Bearings and Rails
Linear bearings and rails are ideal for moving loads through a process with great precision and minimal friction. Linear bearings and rails are used in a variety of applications throughout several different industries and provide the backbone of many industrial applications since they can be implemented in a variety of sizes, accuracy classes, and load capacity, depending on the need of the application and the environment in which the equipment will be in.



Comparison with Other Motion Systems
There are many options for motion systems, and it’s important to consider the needs of your application before making a decision. Linear bearing and rails hold many advantages over other options, due to their reduced friction, high load capacity, precision of movement, and low maintenance.
- Dovetail Linear Guideways: dovetail slides are a type of plain linear bearing that rely on direct contact between the sliding surfaces when supporting a load, unlike linear bearing systems, where the balls and rollers reduce friction between the load-bearing surfaces. Although dovetail guides can work in basic systems, they have higher friction and can break down without proper lubrication.
- Rack and Pinion System: a rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that is comprised of a circular gear (pinion) engaging a linear gear (rack). They work by converting rotational motion into linear motion. Rack and pinion systems, commonly used in the auto industry for steering systems, are very precise due to few pivot points but can have a high failure rate in certain applications.
- Cable-Driven Systems: used often in robotics and several other applications, cable driven systems are controlled by varying the tension in the cable to control motion. The end of the actuator is capable of high speed and acceleration, and cables have the advantage of being lightweight, low-cost, and easy to reconfigure as needed. However, cable-driven systems have limits on usable length and can be prone to breakage in certain industries.
- Lead Screws: Lead screws are a compact and cost-effective solution for light to medium-duty applications. They operate silently with no vibration. However, they are considered to have poor efficiency, making them a suboptimal choice for continuous motion applications.
Linear bearing and rail systems offer more than 10x load and life performance in the same geometric size, with decreased friction and increased precision, making them an optimal choice for many different applications across multiple industries.
Real-World Applications
Considering real-world applications is one of the best ways to assess the benefits of linear bearing and rail systems. The benefits achieved by using linear motion components are seen in many different applications, including improved efficiency, accuracy, and reduced maintenance across the board. Linear guide systems, depending on the customization, are typically easy to install, corrosion-resistant, and able to work in a variety of environments.
CNC Machining Centers
The benefits of using linear bearings and rails in CNC machining centers are many. Linear bearings and rails are crucial in CNC machining centers, enabling high precision and accuracy in cutting, milling, and drilling operations. CNC machines equipped with linear motion components can operate faster, increasing production efficiency with enhanced accuracy. Linear bearings and rails contribute to tight tolerances and repeatability, ensuring precise machining and consistent part quality. The durability of linear bearings and rails reduces the need for frequent maintenance, minimizing downtime, which is essential in the production process.
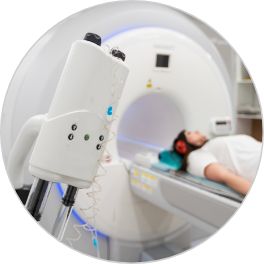
Medical Imaging Equipment
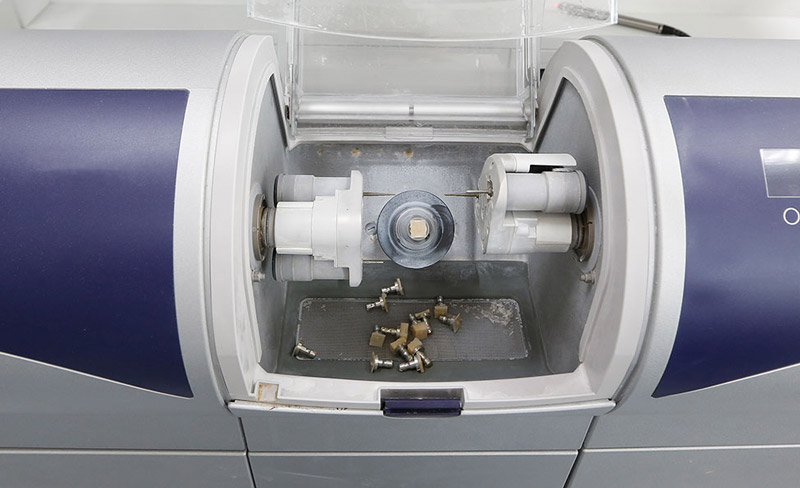 Linear motion components are a mainstay in medical imaging machines like MRI and CT scanners, enhancing patient diagnostics and treatment. Linear bearings and rails contribute to improved efficiency to enable smooth and controlled motion to position imaging components precisely. The high precision of linear motion components ensures accurate image capture and diagnostics with enhanced accuracy. Reliable linear motion systems reduce the risk of critical medical equipment breakdown, leading to improved patient care and reduced maintenance.
Linear motion components are a mainstay in medical imaging machines like MRI and CT scanners, enhancing patient diagnostics and treatment. Linear bearings and rails contribute to improved efficiency to enable smooth and controlled motion to position imaging components precisely. The high precision of linear motion components ensures accurate image capture and diagnostics with enhanced accuracy. Reliable linear motion systems reduce the risk of critical medical equipment breakdown, leading to improved patient care and reduced maintenance.
Automated Material Handling Systems
Linear motion components are integral to warehouse and manufacturing facility conveyor systems and robotic arms, optimizing logistics and production. Linear bearings and rails improve efficiency by enabling the efficient movement of goods and materials, reducing handling time and labor costs. Precise linear motion components ensure accurate positioning and sorting of items. Lower friction and wear in linear motion systems lead to extended equipment lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements, which is optimal in automated machine handling systems.
Aerospace Industry (Aircraft Seat Adjustment)
Linear bearings and rails are used in aircraft seat adjustment mechanisms, enhancing passenger comfort and safety during flights. Linear motion systems have increased efficiency, which allow for quick and precise seat adjustments, improving the in-flight experience for passengers. Passengers can accurately achieve their desired seating positions, enhancing comfort during the flights. In addition, the durability and reliability of linear bearings lessen the need for maintenance, which is vital in aviation for safety and uptime.
3D Printing Machines
Linear motion components are a main component in 3D printers, influencing print quality and speed. Efficiency is improved as linear bearings and rails facilitate smooth and rapid movement of the print head or build platform, reducing overall print time. Precise linear bearings and rails contribute to the accuracy and detail of 3D-printed objects. Low-friction linear components require minimal maintenance, keeping 3D printers operational with limited downtime. Linear guides assist in innovative ultra-fast 3D printing, with speeds exceeding 1000mm/s.
Selection Factors
Although linear bearings and rails have excellent benefits when used in a variety of industries, the impact of their use is dependent on which linear bearings and rails are used in the application. Not every linear system component is created equal, and the better the quality of the linear bearings and rails are, the greater the benefits of their use in the application.
There are several key factors to consider when selecting linear bearings and rails, including load capacity, precision, speed, support arrangements, and environmental conditions. While cost is always a factor, it’s important to look at what the system can offer your application.
Load Capacity
When considering load capacity, rather than just the mass that will need to be supported, consider if there are any moments involved.
Precision
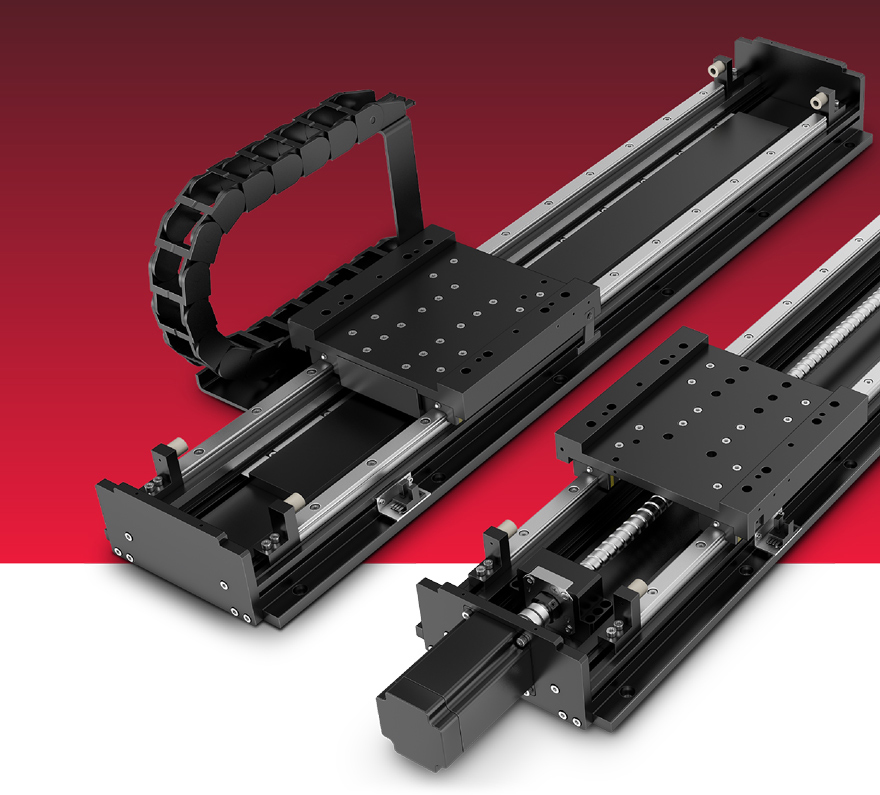 The micron precision of miniature guide rails is different than larger and less precise track rollers.
The micron precision of miniature guide rails is different than larger and less precise track rollers.
Support Arrangement
Will the system need to be fully supported, end-supported, or telescopic?
Environment
Linear guide systems can be designed and modified to work in a variety of environments since many systems can be significantly impacted by dust, dirt, or extreme temperature and will require casing to keep the components fully functional in certain conditions. When selecting bearings and rails, consider the environment. A clean room or vacuum will have different requirements than a manufacturing facility or outside.
Corrosion Resistance
The medical, pharmaceutical, and food industries have varied requirements for corrosion resistance.
Size and Scale
Linear rails and bearings can vary between compact and heavy-duty.
Future Outlook and Industry Innovations
The future outlook for linear bearings and rails is promising, which is driven at least in part by the increasing demand for automation and precision in a wide variety of industries. There have been developments in materials, coatings, and designs that allow linear bearings and rails to be used in an increased number of applications.
There is a growing need for high-performance machinery and equipment, which is developing in tandem with advancements in technology that rely on linear bearings and rails. The ongoing advancements in robotics and industrial automation are driving the demand. Linear rails are crucial in robotic arm movements, 3D printing, and other automated systems that require accurate and repeatable linear motion.
The linear rails market is projected to see substantial growth in the coming years, fueled by this increased demand for automation and precision. With linear bearings and rails providing a precise, quiet, and cost-effective solution, many industries have shifted to linear motion systems relying on linear bearings and rails.
In addition to the increase in demand in general, there is projected to be an increased demand for system solutions, with less design and specification required by the user. Actuators are projected to increase value in linear guide systems by combining multiple linear components, such as linear rails, bearings, and screw drives. As industries continue to innovate, the need for linear bearings and rails will continue to grow, and technological advances will keep the market for these solutions strong. As design and installation time decreases with the advancements in technology, the market growth will increase.
Use Linear Bearings and Rails in Your Next Project
The benefits of using linear bearings and rails are numerous in various industries, but the primary advantages over other systems are the load capacity, travel accuracy, and rigidity. Linear bearings have guaranteed self-lubrication, shock resistance, corrosion resistance, and dirt resistance and are lightweight and quiet during operation.
 Because linear bearings and rails have low maintenance requirements, the system will be reliable and efficient. The technology of linear rail systems continues to evolve, making the potential for continued innovation strong. When considering implementing linear motion solutions in your projects, look to the experts to assist in the planning process. The experts at NSK can guide you through finding the right components to build a custom solution for your application. If you are interested in using a linear rail system in a future project or product, schedule a consultation with the experienced team at NSK to determine how linear bearings and rails can make your project more efficient.
Because linear bearings and rails have low maintenance requirements, the system will be reliable and efficient. The technology of linear rail systems continues to evolve, making the potential for continued innovation strong. When considering implementing linear motion solutions in your projects, look to the experts to assist in the planning process. The experts at NSK can guide you through finding the right components to build a custom solution for your application. If you are interested in using a linear rail system in a future project or product, schedule a consultation with the experienced team at NSK to determine how linear bearings and rails can make your project more efficient.
